
Critical Micelle Concentration
This experiment was adapted by Jonathan Breitzer, Ming-Fong Lye, and George Lisensky from one by K. G. Furton and A. Norelus in J. Chem. Educ. 70, 254-257 (1993).
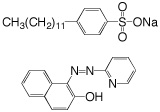
A surfactant has a hydrophobic end and a hydrophilic end. The sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (SDS) used as a surfactant in this experiment has a hydrocarbon chain and a negatively charged charged sulfonate group.

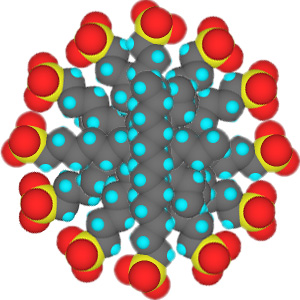
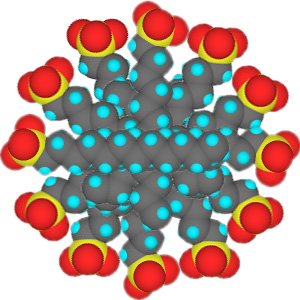
In low concentrations, surfactants in water exist as isolated molecules. Above a certain concentration, called the critical micelle concentration (CMC), they spontaneously form nanosized structures called micelles.
 | 
| 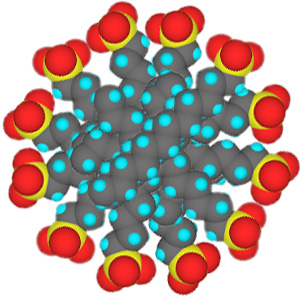 |
Cross section of micelles
When the CMC is reached, the water-insoluble hydrophobic dye 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-naphthol used in this experiment is extracted from indicator paper and dissolves within the micelles to give a color change in the solution. Beyond the CMC the visible absorbance increases as more surfactant is added.
| Procedure | Wear eye protection |
Chemical gloves recommended |
Add a strip of filter paper to 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-naphthol in acetone to absorb the dye. Remove the paper strip and let the acetone evaporate. Place the filter paper strip containing the absorbed water insoluble dye in 100 mL water and stir. No change in color should be observed if the filter paper strip was dry.
Add ten drops or 0.4 mL of surfactant. Wait at least two minutes since the potential color change is not immediate. Before the next addition record the visible absorption spectrum or save a portion for color comparison later. (If the volume is changed by removing solution you will need to know the amount for your calculations.)
Repeat 10-15 times. In the movie only the first addition is shown in real time. The total elapsed time is 40 minutes. How much surfactant must be added to observe a color change in the solution?
The movie shows samples before each addition of surfactant and the finger indicates the sampling order. The critical micelle concentration (CMC) corresponds to the onset of color when the water insoluble dye is extracted into the surfactant micelle. A typical CMC in this system is 0.0016 M.
Graph the absorbance at 470 nm as a function of the surfactant molarity (the calculations are similar to those for an absorption titration). Estimate the critical micelle concentration for sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate.
 |
Equipment |
University of Wisconsin Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
Interdisciplinary Education Group | MRSEC on Nanostructured Interfaces
This page created by George Lisensky, Beloit College. Last modified June 16, 2013 .


