


In 1952, Bloch and Purcell won the Nobel Prize in Physics for the development of the analytical technique known as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an adaptation of NMR for medical diagnostic purposes.
Both NMR and MRI rely on the fact that some atomic nuclei have a magnetic moment associated with their spinning. The most common nuclei studied using NMR are H-1, C-13, F-19 and P-31. Most MRI studies involve the H-1 nuclei in water.
The isotopes listed above have two spin states. When these nuclei are exposed to an external magnetic field, their spins can be parallel or anti-parallel to this external field. Transitions between these two spin states can be induced with energy from radio waves of the proper frequency. A radio frequency (rf) signal is transmitted to the sample, which has been placed in a strong magnetic field. The nuclei of atoms in the sample interact with the rf signal. A rf receiver measures the signal after its interaction with the sample. The analysis of these measurements can help to identify the structure of the sample.
MRI instruments are massive pieces of equipment. Some representative specifications from an instrument manufacturer are collected in the table below.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
to be examined |
cardiac, and spine |
|
cardiac, and spine |
Magnetic resonance imaging - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnetic_resonance_imaging
How Stuff Works: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
http://www.howstuffworks.com/mri.htm
R. de Beer
University of Technology Delft
Department of Applied Physics
P.O. Box 5046, 2600 GA Delft, The Netherlands
Basic
principle of MRI
The Basics of MRI
http://www.cis.rit.edu/htbooks/mri/
For the latest in MRI diagnostic equipment
 |
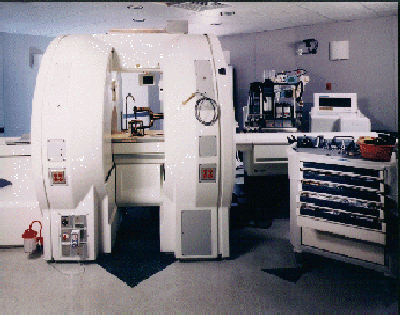
This MRI unit is used in the operating room during surgery. For more information, see:
http://www.gehealthcare.com/usen/mr/products/mrsurgical_suite.html
 |
<NMR/MRI Simulator with Movies!] | [Other NMR Sites>
This page was designed and is maintained by