|
XRD estimation of particle diameter
Diffraction peaks are a result of constructive interference of X-rays reflected by crystal planes. The more planes the sharper the peak so the smaller the crystallite size the broader the diffraction peak.
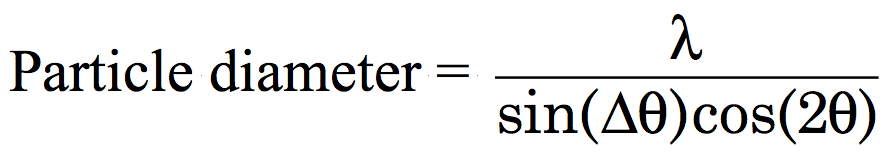 |  |
To analyze the XRD data, open the MDI Jade program.
 Select the file you previously created. The dog icon at the upper left allows you to fetch the most recent scan or you can use the folder icon to find files.
Select the file you previously created. The dog icon at the upper left allows you to fetch the most recent scan or you can use the folder icon to find files.
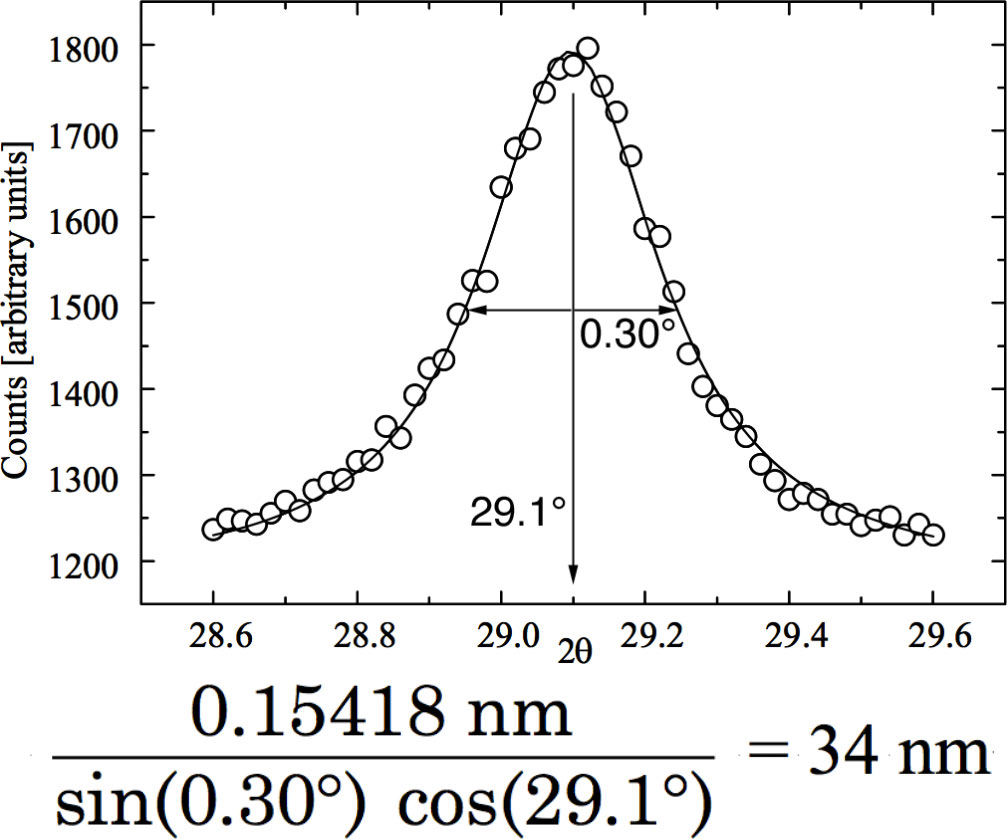
 Click on the icon with the vertical lines to find the peaks and display the d values. To get peak widths for calculating particle size, left click on the double parabola icon to fit a parabola; then right click on the same icon to list the FWHM. Print the window and use the four or five tallest peaks for your analysis.
Click on the icon with the vertical lines to find the peaks and display the d values. To get peak widths for calculating particle size, left click on the double parabola icon to fit a parabola; then right click on the same icon to list the FWHM. Print the window and use the four or five tallest peaks for your analysis.
This page created by George Lisensky, Beloit College.
Last modified August 29, 2022.