

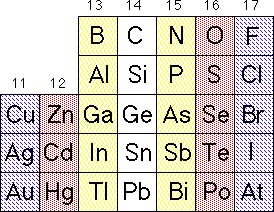
Semiconductors are typically prepared from combinations of elements having crystal structures related to that of diamond and the same average number of valence electrons per atom as the atoms in diamond.
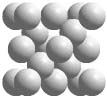
Crystals of carbon, silicon, germanium, and the alpha form of tin from Group 14 of the periodic table all have the diamond structure, whose unit cell is shown above. The diamond unit cell contains all atoms of the same element arranged in a tetrahedral geometry.
Crystals of carbon, silicon, germanium, and the alpha form of tin from Group 14 of the periodic table all have the diamond structure, whose unit cell is shown above. The diamond unit cell contains all atoms of the same element arranged in a tetrahedral geometry.
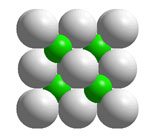
Many complementary pairs of atoms with 1:1 stoichiometry (AZ) and the same average number of valence electrons per atom as the atoms in Group 14 such as ZnS, GaAs, and ZnSe have the zinc blende structure, asshown above. In zinc blende unit cells, there are atoms of two elements,each arranged in a tetrahedral geometry and bonded exclusively to the other kind of atom.
[Spectra] Back | Forward [Solid State Solutions]