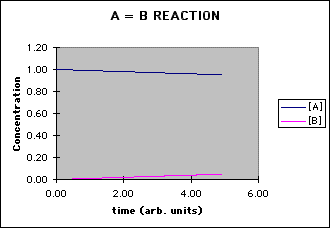
This Microsoft Excel spreadsheet (file AB.xls) uses a primitive differential equation solver to determine the concentration of A and B as a function of time for a simple reaction A = B. The reaction is first order in the forward (A --> B) and reverse direction (B --> A). The parameters that can be adjusted are:
- the initial concentration of A, [A]o found in cell B2
- the initial concentration of B, [B]o found in cell C2
- the rate of the forward (A --> B) reaction kAB found in cell D2
- the rate of the reverse (B --> A) reaction kBA found in cell E2
The output of note consists of the:
- initial ratio of B to A, [B]o /[A]o found in cell F2
- the final ratio of B to A, found in cell G2
- a graph of [A] and [B] vs. time
The rate constant in the forward (kAB) and the reverse direction (kBA) can be adjusted in the range: 0-6. The initial concentration of A and B should fall in the range 0-1.
The following are suggested conditions that you should investigate.
- Keep kAB = kBA and vary the initial concentrations of [A]o and [B]o to determine how these initial concentrations affect the final ratio, [B]/[A] and the time it takes to achieve this ratio.
- Keep [A]o and [B]o constant and vary kAB and kBA to determine how these changes affect the final ratio, [B]/[A] and the time it takes to achieve this ratio.
- Vary the rate constants and initial concentrations and try to determine some general rules for predicting the final [B]/[A] ratio and the time it takes to achieve this ratio.
Reaction Rate and Equilibrium | Origin of Life | ChemConnections